Human papillomavirus (HPV) is one of the most common viral agents in the world.

According to medical statistics, between 80% and 90% of all people on the planet are carriers of HPV, and many of them are not even aware of the presence of papillomavirus in their bodies. This is due to the fact that HPV can remain hidden (inactive) for a long time by penetrating the patient's blood, slowly affecting the basal cells of the epidermis, as well as not showing itself visually. We will try to look at the mechanisms of infection and the symptoms of the disease, as well as understand how to treat human papillomavirus quickly and effectively.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
When answering the topical question of how you can be infected with human papillomavirus, it is important to note three main mechanisms by which the virus agent enters the body:
- Way of communication- in direct contact with the user's epidermis. The risk group includes massage therapists, cosmetologists, dermatologists, etc. ;
- Mediator (household) mechanism- Papilloma virus household items - towels, combs, handles of public transport, etc. implies transmission through;
- Sexual way- Unprotected sex with an infected person provides almost one hundred percent chance of the papillomavirus entering the body, whereas in women, subtypes of the agent, such as type 31 human papillomavirus, can be transmitted even when using a condom.
In men and women, the symptoms of human papillomavirus may not appear until certain conditions or conditions appear. Such factors are considered secondary causes of papillomavirus:
- Decreased immune function;
- Disruption of skin integrity - injuries, micro-cracks, scratches, wounds, etc. ;
- Stress and neuro-emotional overwork;
- Weakening of the body against the background of an inflammatory or infectious process;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Violation of the rules of personal hygiene.
The only symptom of the papilloma virus can be considered the formation of specific skin neoplasms, which are mostly benign, but require mandatory medical supervision. In the presence of at least one of the above factors, the patient develops skin growth within 1-6 months after the initial infection. The incubation period of papillomavirus lasts so long.
Why are different types of human papillomavirus dangerous?

To determine how to get rid of human papillomavirus and whether it is worth taking therapeutic measures in general, we will understand what this viral agent can be dangerous and how serious the consequences can be. Often people do not pay enough attention to skin growths such as papillomas and warts, they consider them harmless defects. Only the noticeable (frontal) localization of the neoplasm, which causes aesthetic problems, may prompt the patient to consult a specialist. Meanwhile, some types of human papillomavirus are considered precancerous conditions and can develop into malignant tumors.
In modern medicine, there are about 120 types of papillomavirus that determine the location, size and oncogenicity of epidermal growth. We will try to understand which species can be considered only an aesthetic defect and which require immediate treatment:
- Types 1, 2, 4 of the papilloma virus.The viral agent leads to the formation of plantar warts, which can grow over time and spread to healthy tissues, making it difficult for the patient to move;
- Papillomavirus types 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57.Causes common or vulgar warts that most commonly affect the skin of the hands.
- Papilloma virus 3, 10, 28, 49 types.This is the main reason for the appearance of straight warts, which affect most children and adolescents, for which they received a second name - young;
- HPV type 7.Forms special papillomas in the hands of an infected person called "butcher's warts";
- Papilloma virus types 2, 3, 5, 8-10, 12, 14, 15, 17, 19, 20, 36, 37, 46, 47 and 50.A large group of viral agents that cause epidermodysplasia veruciform, as well as exceptionally benign formations;
- Human papillomavirus types 6 and 11, as well as types 42 and 54.A more dangerous group of HPV that causes genital herpes in the genitals and mucous membranes. Such growths may undergo malignant transformation;
- Papillomavirus 16, 18 and most subtypes 30-67 species.This group of viral agents has a high level of oncogenicity in the genitals. Thus, in women, type 33 papillomavirus, as well as type 18 papillomavirus, causes flat warts and cervical dysplasia, which can lead to cervical cancer;
- Papilloma virus type 51, as well as types 45, 52, 54, 56, 66, 68.Human papillomavirus type 52 and other aggressive agents in this group can cause cervical or vaginal cancer, as well as oncology of the external genitalia and anus.
It should be noted that these are not all subtypes of HPV known to science, but the types listed above can be confidently classified as the most common.
How to detect human papillomavirus in women and the stronger sex?
Diagnosis is a mandatory step to see a doctor in case of papillomas on the skin or mucous membranes. This is due to the risk of confusing papilloma with another skin problem. Although asymptomatic in most cases, human papillomavirus in women is often detected only by routine or other reasons, such as a gynecological examination.
Skin growth can be distinguished by a simple examination confirmed by microscopic analysis of epithelial fragments. At the same time, the final diagnosis can be made only after PCR diagnosis, which allows to determine the presence of papilloma virus in the patient's blood. If you suspect a malignant course of genital papillomas, an additional test is often prescribed - a tissue biopsy.
Human papillomavirus - treatment
When answering the question of how to treat the papilloma virus, one must first consider that simply removing a skin neoplasm will not solve the problem once and for all, because the viral agent remains in the blood. Unfortunately, to date, medicine has not developed an effective way to completely cleanse the human body of the virus, but strengthening immunity and rational hygienic care do not allow HPV to actively multiply and be accompanied by the appearance of skin defects.
There are two main directions for the removal of papillomas of different localization:
- Treatment of human papillomavirus with folk remedies;
- Apparatus removal of benign neoplasms.
Treatment of papillomavirus with folk remedies
Folk recipes suggest the use of fresh celandine juice, as well as iodine and vinegar solutions as agents that burn papillomas. Such methods are based on the simple application of an agent to a neoplasm with subsequent rejection. Keep in mind that this practice has limited effectiveness and can cause scars or scars. A milder option is regular application of garlic to cut skin growth, which may not provide the desired result, but certainly will not harm the patient's health.
Wormwood, dandelion, tricolor violet, etc. The use of decoctions and infusions of herbs such as strengthen the immune system and provide natural resistance to HPV. Treatment of human papillomavirus at home can also be done with the help of special pharmacy ointments, creams and patches.
How to treat human papilloma with hardware methods
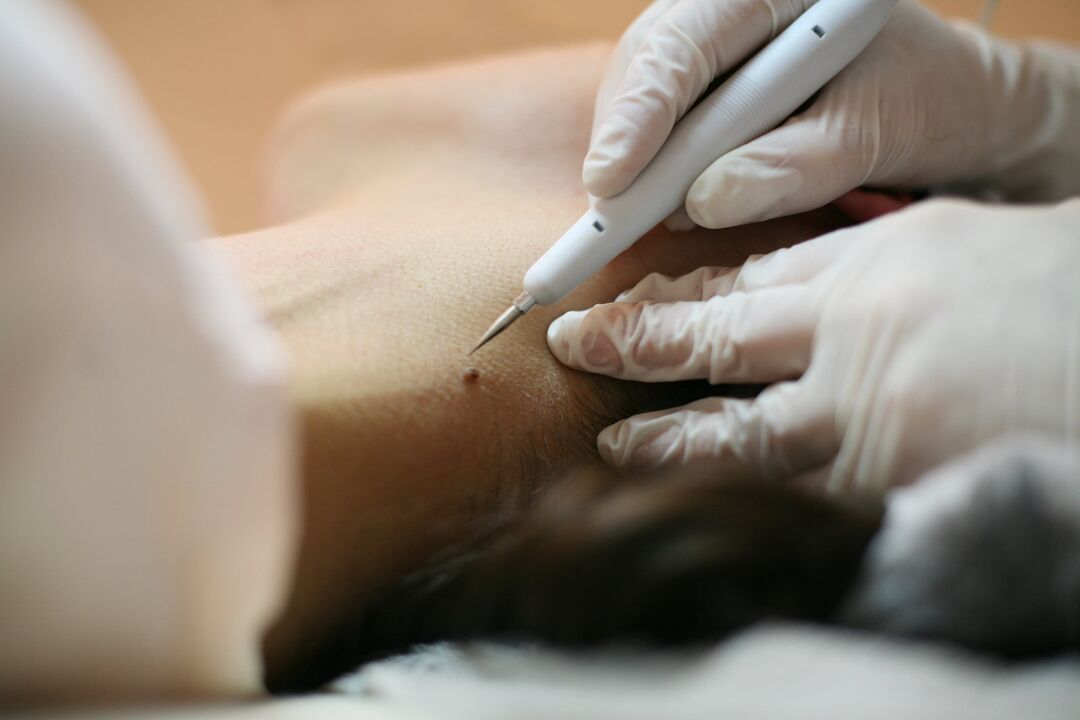
Modern medicine offers several effective device options to get rid of the papilloma virus from a patient, but laser destruction of neoplasms is considered the "gold standard" in this regard. The method is effective, painless and simple. The manipulation takes only a few minutes without affecting the surrounding epidermal structures. This approach will not only protect the patient from unwanted wounds and scars, but also significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
The multidisciplinary clinic offers its clients laser removal of papillomas and warts anywhere using the latest medical equipment. The specialties of our specialists are complemented by many years of experience and an individual approach to each client.















































































